ADC Conjugation (ez-ADiCon™)
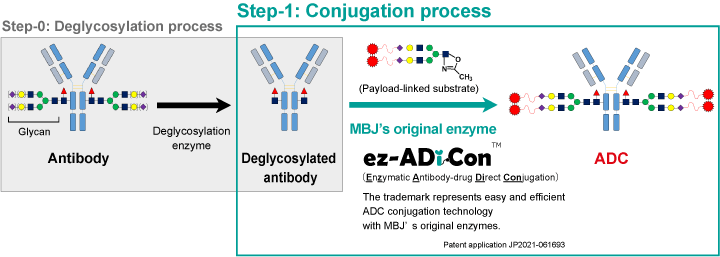
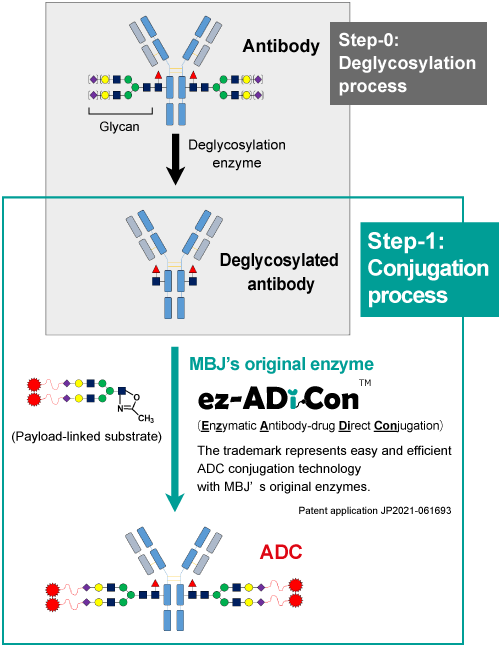
ez-ADiCon™ (ADC conjugation technology based on MBJ's original enzyme) comprises deglycosylation and conjugation processes for ADC synthesis. In the deglycosylation process (Step-0 in the figure below), the glycans of an antibody are enzymatically cleaved. In the following conjugation process (Step-1), payload-linked substrates are attached on the antibody with a MBJ's original enzyme. The payload-linked substrates are assembled in advance by linking payloads at the terminus of glycan via a linker.
MBJ's ADC Conjugation Technology
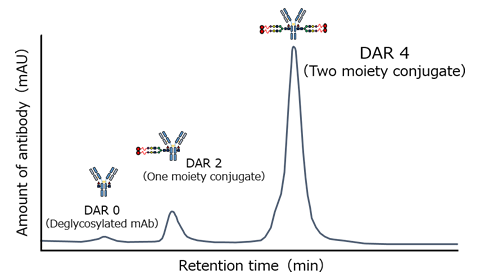
ez-ADiCon™ enables generation of homogenous ADC with DAR (drug-to-antibody ratio) close to theoretical maximum. Compared with products and technologies from other companies, MBJ's technology is superior in site-specificity, high DAR and homogeneity. The payload-linked glycans are also homogenous. These technical features facilitate well-controlled quality management.
Drug load distribution of ADC prepared with ez-ADiCon™
| Payload-linked substrate |
Conversion rate (%) |
Residual rate (%) |
DAR* | DAR Reaction rate** |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DAR4 | DAR2 | DAR0 | |||
| A | 93 | 7 | 0 | 3.9 | 97% |
| B | 79 | 21 | 0 | 3.6 | 90% |
DAR* drug-to-antibody ratios
DAR Reaction rate** DAR/Theoretical Max. DAR x 100
Comparison of ADC conjugation technologies
| Market and Approved | Conjugation technology | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Properties | Product A | Product B | Technology C | Technology D | ez-ADiCon™ |
| Site-specificity | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Homogeneity (DAR) |
Hetero | Homo | Homo | Homo | Homo |
| Glycoform | Hetero | Hetero | Hetero | Homo (Payload-linked) |
Homo (Payload-linked) |
| Conjugation process |
Chemical | Chemical | Chemical | Enzyme+ Chemical |
Enzyme |
| Mutagenesis of antibody |
No | No | Yes | No | No |

